

Next: First Catalog Sources
Up: The Second EGRET Catalog
Previous: Catalog Construction
The entries in the catalog (Table 4) are given in order of increasing right ascension. For each source, multiple entries are given. For each source, the first entry is the one from which the source position was derived. In almost all cases, this is the detection with the highest statistical significance. Other entries in the table give the results for the summed maps for Phase 1, Phase 2, and Phase 1 + 2 and for all viewing periods meeting the following criteria: (1) the source was within 30 of the EGRET pointing direction (There is one exception to the 30
of the EGRET pointing direction (There is one exception to the 30 cutoff: the highest-significance detection of 2EG J1158+2906 was in viewing period 206.0, in which the source was 31
cutoff: the highest-significance detection of 2EG J1158+2906 was in viewing period 206.0, in which the source was 31 from the axis); and (2) the exposure was large enough to derive a meaningful flux or upper limit.
For each observation with
from the axis); and (2) the exposure was large enough to derive a meaningful flux or upper limit.
For each observation with 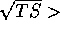 3, the excess is presented as a flux with its uncertainty. For lower values of the
3, the excess is presented as a flux with its uncertainty. For lower values of the 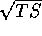 , the result is presented as an upper limit. Each analysis was carried out independently; therefore, the sum of counts for a source from individual viewing periods does not necessarily match precisely the counts from the summed map.
, the result is presented as an upper limit. Each analysis was carried out independently; therefore, the sum of counts for a source from individual viewing periods does not necessarily match precisely the counts from the summed map.
The flux uncertainties shown are statistical only. For all except the brightest sources or those in confused regions, the statistical uncertainty is larger than any systematic uncertainties. Systematic effects include the uncertainty in the calibration (Thompson et al. 1993a) as a function of energy and angle within the instrument and the gradual change in operating performance of EGRET as the spark chamber gas ages. A first order correction to this latter effect has been included. At this time, we recommend that a residual uncertainty of 10% should be attached to any flux value, in addition to the statistical uncertainty. Sources in confused regions may also have significant uncertainties due to the overlapping point spread functions. The fluxes for such sources (e.g. 2EG J1801-2312 and 2EG J1811-2339) should not be considered independent of each other, particularly in searching for time variability.
The primary catalog is Table 4. The columns in the table are:
Name -- based on the J2000 coordinates for the best position
of the source, following the IAU naming convention (PASP 102, 1231). It should be emphasized that the measured positions are generally not as precise as the name might suggest.
RA and Dec -- the J2000 coordinates measured by EGRET, in degrees.
l and b -- the galactic coordinates measured by EGRET
A and B are the semimajor and semiminor axes respectively of an ellipse fitted to the 95% confidence error contour, in
arcmin. 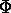 is the position angle of the major axis, measured eastward from north in celestial coordinates, in degrees. A * indicates that the error box is not well
represented by an ellipse.
is the position angle of the major axis, measured eastward from north in celestial coordinates, in degrees. A * indicates that the error box is not well
represented by an ellipse.
Morphology: E=extended source (applies only to the Large Magellanic Cloud); em=possibly extended source or multiple sources (based on source location maps inconsistent with a single point source or poor fit to the calibrated PSF);
C=source confusion may affect flux, significance, or
position. Sources with no entry in this column are
consistent with the EGRET point spread function for a single source.
F -- the flux (E>100 MeV) in 10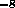 photons/cm
photons/cm s, or upper limit in the same units for observations in which the source was not detected
s, or upper limit in the same units for observations in which the source was not detected
 F -- the 1
F -- the 1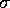 statistical uncertainty in the flux
statistical uncertainty in the flux
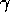 -- the photon number spectral index F(E)
-- the photon number spectral index F(E) 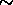 E
E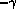 in the energy range 100-2000 MeV. Spectra have not been determined for all sources. The flux F for most sources was determined assuming an energy spectrum with a photon number index of 2.
in the energy range 100-2000 MeV. Spectra have not been determined for all sources. The flux F for most sources was determined assuming an energy spectrum with a photon number index of 2.
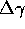 -- the 1
-- the 1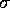 uncertainty in the spectral index
uncertainty in the spectral index
Counts -- the number of E>100 MeV photons represented by the flux or upper limit. The uncertainty in the counts is proportional to  F/F.
F/F.
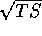 -- the statistical significance of the E>100
MeV detection. It is approximately equal to the statistical
-- the statistical significance of the E>100
MeV detection. It is approximately equal to the statistical
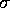 for a single measurement at a fixed position.
for a single measurement at a fixed position.
VP -- the viewing period of the Observation. P1 = Phase 1
summed map 4/91 - 11/92; P2 = Phase 2 summed map 11/92 -
9/93; P12 = Phase 1 + 2 summed map 4/91 - 9/93; 0.2+ is the sum of viewing periods 0.2 - 0.5, all of which covered the same region of the sky during the verification phase of the mission; 36.+ is the sum of 36.0 and 36.5, which cover the same region of the sky.
ID P=pulsar (indicates detection of pulsed gamma radiation); G=galaxy (the LMC is the only such object in the catalog); A=active galactic nucleus; a=active galactic nucleus (marginal). In this catalog, a marginal identification is defined as one in which the candidate object lies near but outside the 95% uncertainty contour. Note that this is a different notation from that used in the first EGRET catalog, which distinguished identifications by their statistical significance.
Other names -- the source name from the first EGRET catalog ([Fichtel et al. 1994b])
or other gamma-ray references. In some cases, the source position has moved from that given in earlier references. For identified sources, the name or names of the object is given in this column.
Notes -- positional coincidences with objects of interest which might be the gamma-ray source, or special information about the detection.
References -- previous EGRET references to the source.


Next: First Catalog Sources
Up: The Second EGRET Catalog
Previous: Catalog Construction
Sergej A.Trushkin
Sun Dec 8 10:02:02 MSK 1996
 of the EGRET pointing direction (There is one exception to the 30
of the EGRET pointing direction (There is one exception to the 30 cutoff: the highest-significance detection of 2EG J1158+2906 was in viewing period 206.0, in which the source was 31
cutoff: the highest-significance detection of 2EG J1158+2906 was in viewing period 206.0, in which the source was 31 from the axis); and (2) the exposure was large enough to derive a meaningful flux or upper limit.
For each observation with
from the axis); and (2) the exposure was large enough to derive a meaningful flux or upper limit.
For each observation with 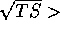 3, the excess is presented as a flux with its uncertainty. For lower values of the
3, the excess is presented as a flux with its uncertainty. For lower values of the 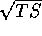 , the result is presented as an upper limit. Each analysis was carried out independently; therefore, the sum of counts for a source from individual viewing periods does not necessarily match precisely the counts from the summed map.
, the result is presented as an upper limit. Each analysis was carried out independently; therefore, the sum of counts for a source from individual viewing periods does not necessarily match precisely the counts from the summed map.
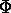 is the position angle of the major axis, measured eastward from north in celestial coordinates, in degrees. A * indicates that the error box is not well
represented by an ellipse.
is the position angle of the major axis, measured eastward from north in celestial coordinates, in degrees. A * indicates that the error box is not well
represented by an ellipse.
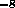 photons/cm
photons/cm s, or upper limit in the same units for observations in which the source was not detected
s, or upper limit in the same units for observations in which the source was not detected
 F -- the 1
F -- the 1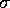 statistical uncertainty in the flux
statistical uncertainty in the flux
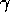 -- the photon number spectral index F(E)
-- the photon number spectral index F(E) 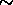 E
E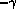 in the energy range 100-2000 MeV. Spectra have not been determined for all sources. The flux F for most sources was determined assuming an energy spectrum with a photon number index of 2.
in the energy range 100-2000 MeV. Spectra have not been determined for all sources. The flux F for most sources was determined assuming an energy spectrum with a photon number index of 2.
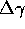 -- the 1
-- the 1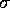 uncertainty in the spectral index
uncertainty in the spectral index
 F/F.
F/F.
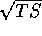 -- the statistical significance of the E>100
MeV detection. It is approximately equal to the statistical
-- the statistical significance of the E>100
MeV detection. It is approximately equal to the statistical
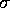 for a single measurement at a fixed position.
for a single measurement at a fixed position.